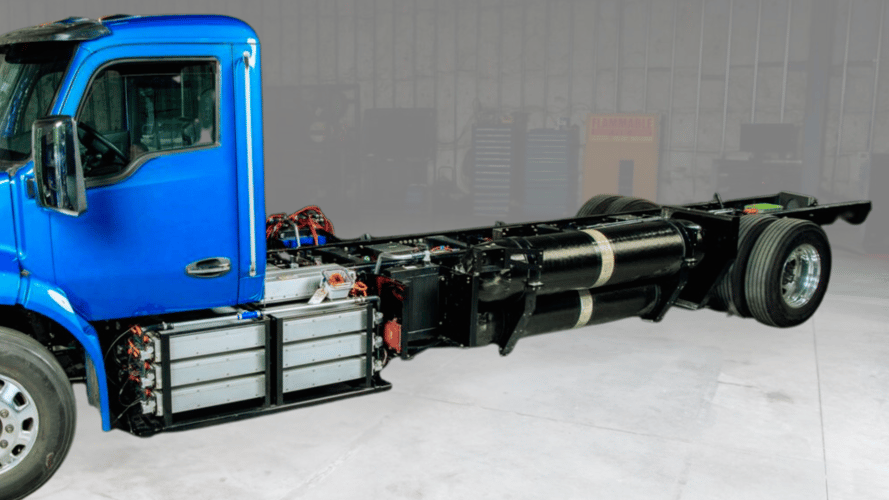
Commercial transport integrator, Fontaine Modification, together with Ballard Power Systems and a consortium that includes Forsee Power and Linamar, is developing a Class 6 fuel cell electric truck to meet the demands of 'middle-mile' delivery logistics - which is expected to be the first of its kind available in the United States.
A pilot test fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) will be completed this spring, and will then undergo six months of trials, beginning in the third quarter of 2025, while being operated over regular routes by the truck’s first customer - a large commercial fleet seeking a FCEV designed for ‘middle-mile’ delivery.
Once successful field trials are completed, the consortium anticipates that regular production of the truck will begin by the end of 2026.
Serving as the vehicle and systems integrator, Fontaine Modification is assembling the FCEV on a gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) straight truck chassis at its flagship modification facility in Charlotte, N.C. Ballard provides the project's power through its FCmove®-XD 120kW fuel cell engine, Forsee Power delivers the high-voltage battery system, and Linamar is responsible for the FCEV’s eAxle.
Ballard is showcasing the value of its latest fuel cell engine, the FCmove®-XD, in North America for the first time.  The module provides an easy integration platform for vehicle OEMs and integrators and is designed to deliver up to 60% fuel efficiency with volumetric power density of 0.36kW/L while lasting over 30,000 hours in operation. Developed for volume production, the FCmove®-XD is commercially established for scalability, and provides a competitive total cost of ownership.
The module provides an easy integration platform for vehicle OEMs and integrators and is designed to deliver up to 60% fuel efficiency with volumetric power density of 0.36kW/L while lasting over 30,000 hours in operation. Developed for volume production, the FCmove®-XD is commercially established for scalability, and provides a competitive total cost of ownership.
For FCEVs, balancing and optimizing fuel cell and battery power is essential to achieve maximum efficiency, performance, and operational longevity. Depending on the situation, the FCEV is driven by the battery, by the fuel cell, or by both if additional power is required. Offering a multitude of benefits to operators, fleets, and drivers, the collaboration delivers a solution able to meet the technical needs of long distance - with power peaks on highways - and local deliveries, optimizing the cost.
The vehicle's low-maintenance design helps fleet operators reduce operational costs, while its quiet propulsion system provides a smoother and less intrusive experience for drivers and other road users. Regenerative braking recoups energy that might otherwise be lost, boosting the vehicle's overall efficiency; while wear and tear is also reduced on critical components, leading to lower maintenance costs and improved durability.