
Data centers and cloud computing are among today’s fastest-growing businesses. But they consume power on a massive scale—in fact, power can represent over 50% of a data center’s operating costs. And data centers cannot go down: many of them are considered critical infrastructure and require backup power capability on the same scale as their primary power system.
A growing problem is the fossil fuel footprint of these power systems. Today, the power sources for most backup power systems are diesel-fueled generators. But how can data centers meet their enormous power demands—for primary and backup power—without fossil fuels?
In this article, you’ll learn about the operational and sustainability benefits of hydrogen fuel cells for megawatt-scale, zero-emission power.
Only fuel cells meet the demand for grid-scale zero-emission power backup
Government and industry regulators are increasingly aware of the need to transition away from fossil fuels, and many have announced net-zero objectives that come into effect very soon. In urban areas, the restrictive emissions regulations are the most stringent, but the pressure to adopt more sustainable solutions is increasing in every region.
Microsoft, with its Azure Cloud Services is one of the organizations that’s leading the way and has committed to becoming carbon negative by 2030. By 2050 the company plans to remove more carbon from the environment than it has emitted since its founding.
Additionally, most large-scale data centers require onsite uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and backup power systems that must provide backup power for 24 to 48 hours.
To meet these requirements, the industry needs an alternative power source that’s reliable, with the ability to store large quantities of energy, while providing a zero carbon footprint.
Hydrogen PEM fuel cells are the answer. Fuel cells are the only viable solution that meets the key requirements of upcoming mandates:
- PEM fuel cells are 100% zero-emission: They improve local air quality.
- PEM fuel cells are sustainable: They meet the most stringent requirements for a sustainable supply chain.
- PEM fuel cells are reliable: Fuel cells provide a high level of reliability and availability, supplying uninterrupted power. With gigawatts of fuel cell engines and systems produced to date, the technology has demonstrated its reliability in challenging operating conditions such as in buses and trucks.
How do hydrogen fuel cells compare to battery-based backup systems?
Rechargeable battery systems often come to mind as a possible backup solution. The truth is, battery technologies are not viable—for several reasons.
Limitation of battery backups:
- Short duration: Most battery-based solutions store energy from one to four hours before needing to recharge. Extension of backup times requires more battery, where it only requires more fuel (hydrogen) for a fuel cell system.
- High cost: Longer-lasting solutions (twelve hours or more of continuous power) are prohibitively expensive.
- High space requirements: The physical space required by a grid-scale battery backup system is prohibitive, especially in urban areas where real-estate costs are high.
- Not sustainable: The production of lithium batteries is energy-intensive, with a high carbon footprint.
Disposal of lithium batteries is an environmental concern.
In summary, long-duration battery backup systems fail key criteria: they cannot economically provide the power required, and they are not environmentally sustainable. Fuel cells, on the other hand, deliver grid-scale power in a smaller footprint and are recyclable/refurbishable.
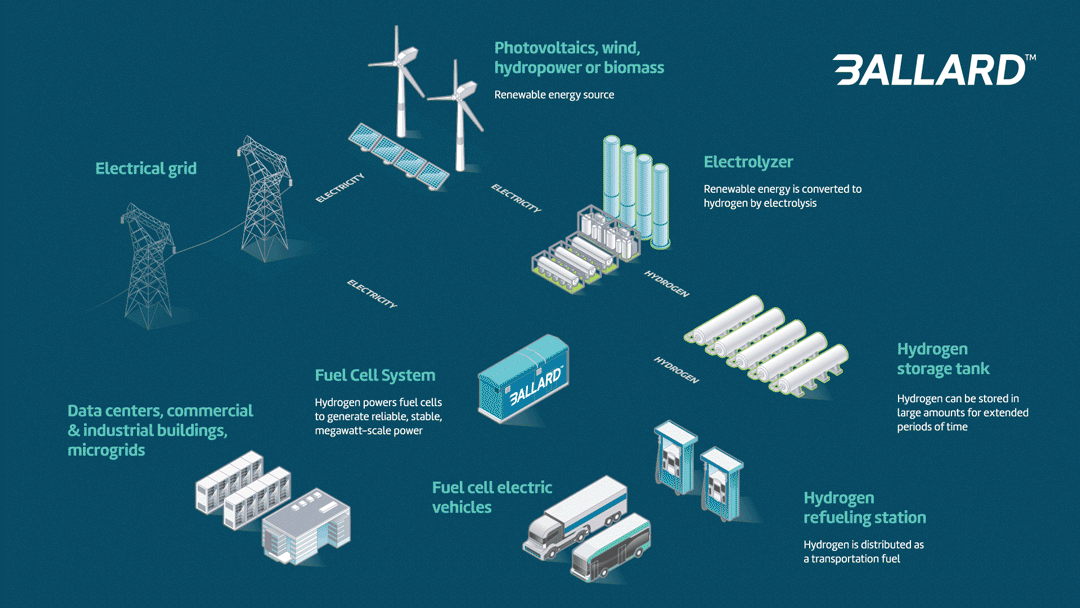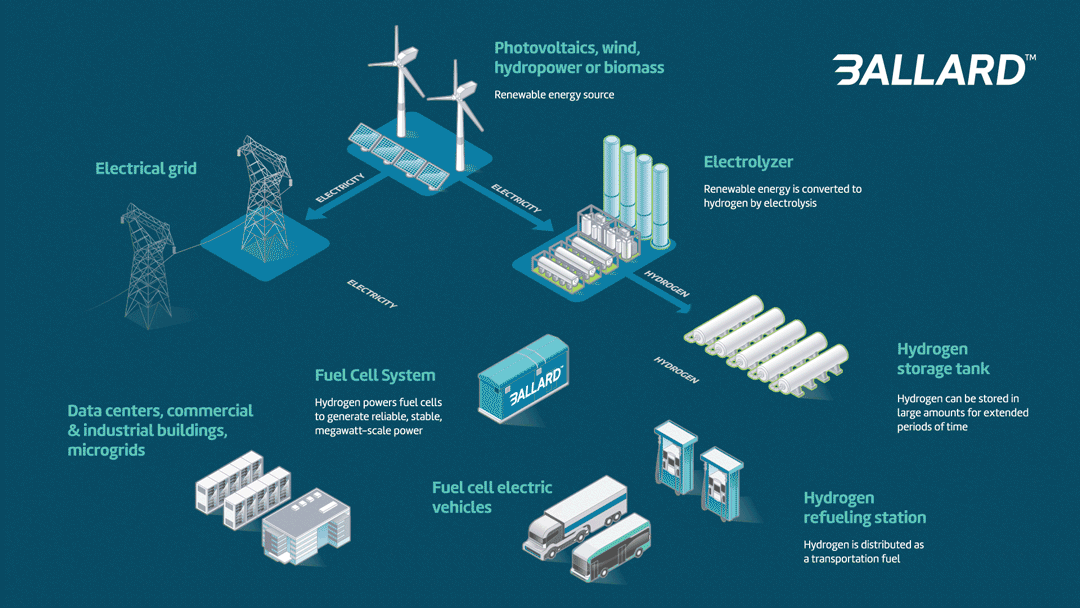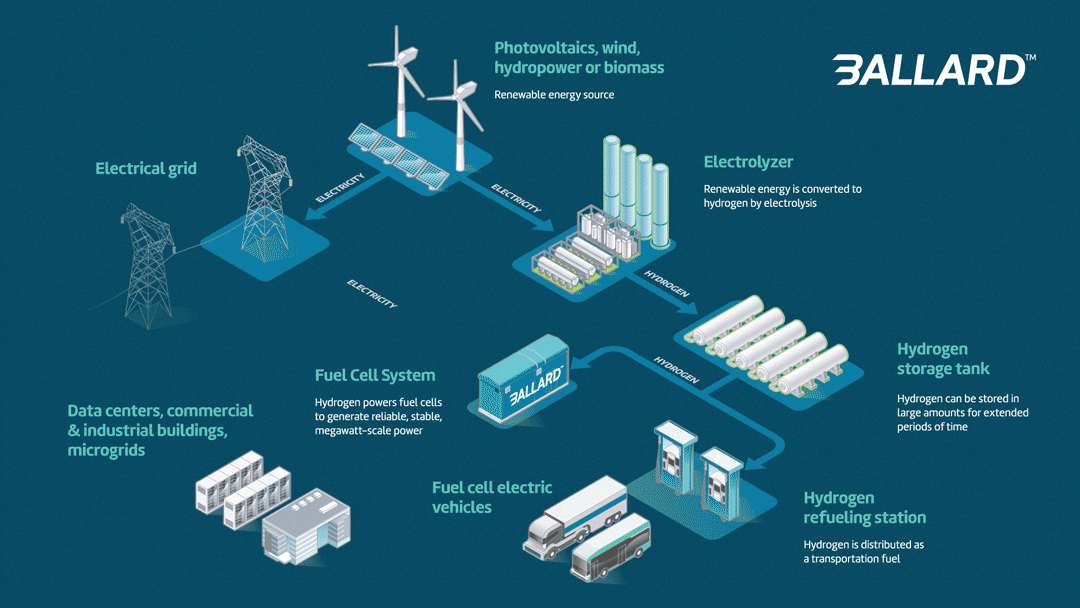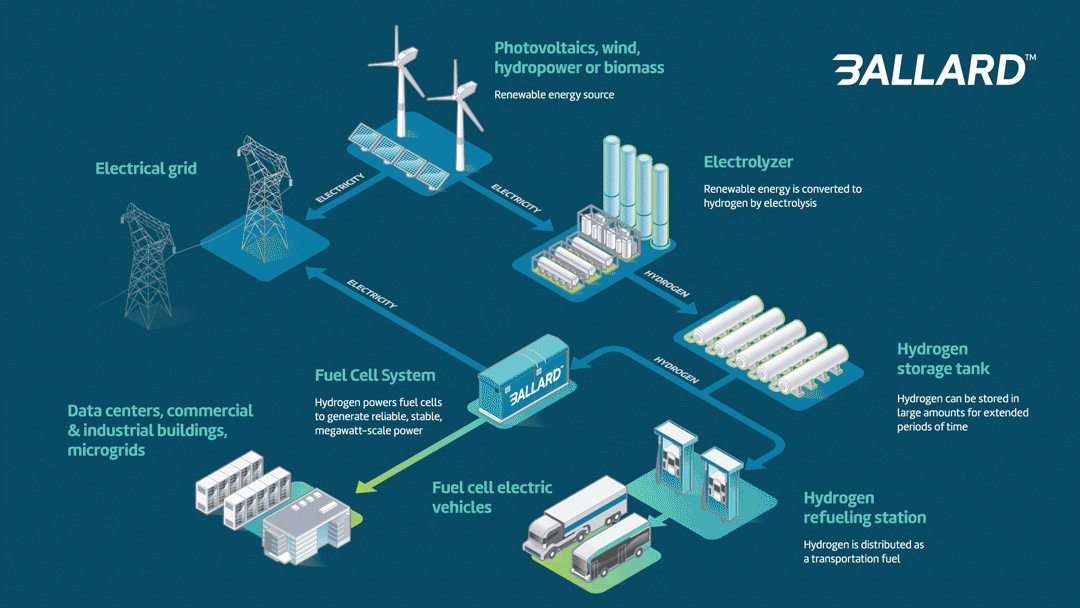
Fuel cell power system advantages:
- Long duration power: Hydrogen fuel cells can be refueled while in operation, meaning that they can run nonstop. A stationary fuel cell power system can function as a backup or as a primary source of grid-scale power.
- Smaller footprint: A grid-scale hydrogen fuel cell solution has a far smaller footprint than comparable battery storage. Ballard systems are the most compact available.
- Recyclable: Ballard’s process for recycling and refurbishing fuel cells is well established; the cell’s bipolar plates are reused many times, and 95% of the platinum in the membrane electrode assembly is reclaimed.

The Ballard Megablock: Today’s only commercially viable zero-emission system for backup power on a megawatt scale
Among today’s power backup solutions, the only commercially viable zero-emission system for megawatt-level stationary power is the Ballard Megablock. Each Megablock can hold up to six 200kW modules to produce a total of up to 1.2MW of rated power. Each module can operate individually to maximize redundancy.
The Ballard Megablock:
- The most compact footprint per megawatt
- Fast ramp-up to power: from stand-by to 100% in less than 30 seconds
- No hydrogen consumed in standby mode
- 50%-60% efficiency at part power
- Regulated DC or AC power from 350-720 VdcV
- Complies with EU, ATEX, and CSA standards for stationary fuel cell power generation
Final thoughts
The time for data centers to transition away from fossil fuels is now. Today, fuel cells offer the cleanest, best-performing fossil fuel alternative for stationary power—whether for backup or primary power generation. Compared to batteries, fuel cells offer more cost-effective, more practical, sustainable, zero-emission power at the megawatt scale.